현재 방탈출 예약 페이지의 로그인은 jwt를 사용해 인증을 하고 있고, cookie에 jwt를 담아서 보내주는 형식이다. 즉, API 요청 과정에서 쿠키에 토큰을 담아 보내줘야 한다.
로그인을 하면 위와 같이 cookie에 token을 담아준다.

해당 값을 디코딩해보면 다음과 같다.

그렇다면, 페이로드를 수정해서 다시 인코딩 후 토큰을 사용하면 어떻게 될까?
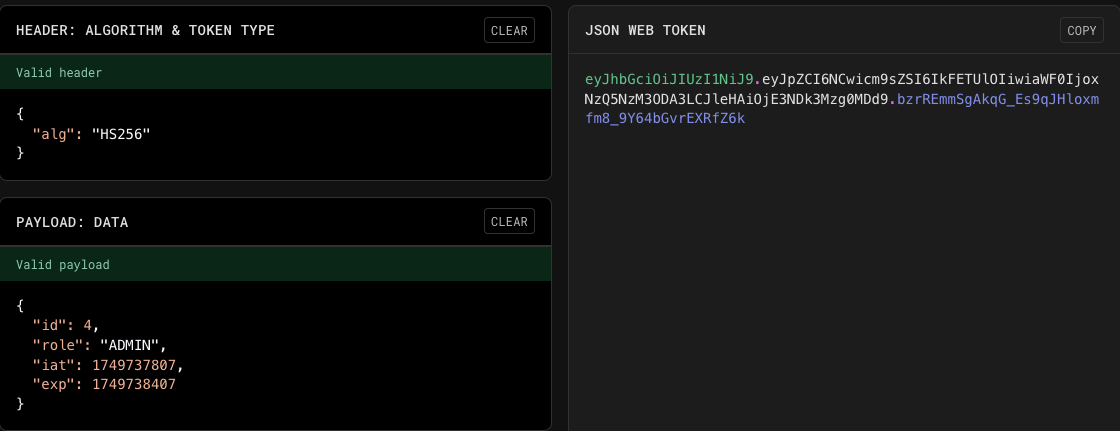
ADMIN 계정인 id = 4, ROLE = ADMIN으로 변경해 봤다. 과연 페이로드를 admin으로 조작한 이 토큰을 사용할 수 있을까?

우선 조작하기 전의 토큰은 디코딩이 잘 되는것을 확인할 수 있다. 조작된 토큰은 어떨까??

오.. SignatureException이 발생한다!
JJWT 라이브러리의 코드를 살펴보면, SignatureException이 뭔지 잘 설명이 되어있다.

그리고 정확히 에러가 발생하는 부분은 다음과 같다.
if (!validator.isValid(jwtWithoutSignature, base64UrlEncodedDigest)) {
String msg = "JWT signature does not match locally computed signature. JWT validity cannot be " +
"asserted and should not be trusted.";
throw new SignatureException(msg);
}
내부 코드를 통해서 시그니처를 확인하고, 만약 시그니처가 조작되었다면 SignatureException을 던지는 코드다.
파싱 하는 부분의 전체 코드
@Override
public Jwt parse(String jwt) throws ExpiredJwtException, MalformedJwtException, SignatureException {
Assert.hasText(jwt, "JWT String argument cannot be null or empty.");
String base64UrlEncodedHeader = null;
String base64UrlEncodedPayload = null;
String base64UrlEncodedDigest = null;
int delimiterCount = 0;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(128);
for (char c : jwt.toCharArray()) {
if (c == SEPARATOR_CHAR) {
CharSequence tokenSeq = Strings.clean(sb);
String token = tokenSeq!=null?tokenSeq.toString():null;
if (delimiterCount == 0) {
base64UrlEncodedHeader = token;
} else if (delimiterCount == 1) {
base64UrlEncodedPayload = token;
}
delimiterCount++;
sb.setLength(0);
} else {
sb.append(c);
}
}
if (delimiterCount != 2) {
String msg = "JWT strings must contain exactly 2 period characters. Found: " + delimiterCount;
throw new MalformedJwtException(msg);
}
if (sb.length() > 0) {
base64UrlEncodedDigest = sb.toString();
}
if (base64UrlEncodedPayload == null) {
throw new MalformedJwtException("JWT string '" + jwt + "' is missing a body/payload.");
}
// =============== Header =================
Header header = null;
CompressionCodec compressionCodec = null;
if (base64UrlEncodedHeader != null) {
String origValue = TextCodec.BASE64URL.decodeToString(base64UrlEncodedHeader);
Map<String, Object> m = readValue(origValue);
if (base64UrlEncodedDigest != null) {
header = new DefaultJwsHeader(m);
} else {
header = new DefaultHeader(m);
}
compressionCodec = compressionCodecResolver.resolveCompressionCodec(header);
}
// =============== Body =================
String payload;
if (compressionCodec != null) {
byte[] decompressed = compressionCodec.decompress(TextCodec.BASE64URL.decode(base64UrlEncodedPayload));
payload = new String(decompressed, Strings.UTF_8);
} else {
payload = TextCodec.BASE64URL.decodeToString(base64UrlEncodedPayload);
}
Claims claims = null;
if (payload.charAt(0) == '{' && payload.charAt(payload.length() - 1) == '}') { //likely to be json, parse it:
Map<String, Object> claimsMap = readValue(payload);
claims = new DefaultClaims(claimsMap);
}
// =============== Signature =================
if (base64UrlEncodedDigest != null) { //it is signed - validate the signature
JwsHeader jwsHeader = (JwsHeader) header;
SignatureAlgorithm algorithm = null;
if (header != null) {
String alg = jwsHeader.getAlgorithm();
if (Strings.hasText(alg)) {
algorithm = SignatureAlgorithm.forName(alg);
}
}
if (algorithm == null || algorithm == SignatureAlgorithm.NONE) {
//it is plaintext, but it has a signature. This is invalid:
String msg = "JWT string has a digest/signature, but the header does not reference a valid signature " +
"algorithm.";
throw new MalformedJwtException(msg);
}
if (key != null && keyBytes != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("A key object and key bytes cannot both be specified. Choose either.");
} else if ((key != null || keyBytes != null) && signingKeyResolver != null) {
String object = key != null ? "a key object" : "key bytes";
throw new IllegalStateException("A signing key resolver and " + object + " cannot both be specified. Choose either.");
}
//digitally signed, let's assert the signature:
Key key = this.key;
if (key == null) { //fall back to keyBytes
byte[] keyBytes = this.keyBytes;
if (Objects.isEmpty(keyBytes) && signingKeyResolver != null) { //use the signingKeyResolver
if (claims != null) {
key = signingKeyResolver.resolveSigningKey(jwsHeader, claims);
} else {
key = signingKeyResolver.resolveSigningKey(jwsHeader, payload);
}
}
if (!Objects.isEmpty(keyBytes)) {
Assert.isTrue(algorithm.isHmac(),
"Key bytes can only be specified for HMAC signatures. Please specify a PublicKey or PrivateKey instance.");
key = new SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, algorithm.getJcaName());
}
}
Assert.notNull(key, "A signing key must be specified if the specified JWT is digitally signed.");
//re-create the jwt part without the signature. This is what needs to be signed for verification:
String jwtWithoutSignature = base64UrlEncodedHeader + SEPARATOR_CHAR + base64UrlEncodedPayload;
JwtSignatureValidator validator;
try {
validator = createSignatureValidator(algorithm, key);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
String algName = algorithm.getValue();
String msg = "The parsed JWT indicates it was signed with the " + algName + " signature " +
"algorithm, but the specified signing key of type " + key.getClass().getName() +
" may not be used to validate " + algName + " signatures. Because the specified " +
"signing key reflects a specific and expected algorithm, and the JWT does not reflect " +
"this algorithm, it is likely that the JWT was not expected and therefore should not be " +
"trusted. Another possibility is that the parser was configured with the incorrect " +
"signing key, but this cannot be assumed for security reasons.";
throw new UnsupportedJwtException(msg, e);
}
if (!validator.isValid(jwtWithoutSignature, base64UrlEncodedDigest)) {
String msg = "JWT signature does not match locally computed signature. JWT validity cannot be " +
"asserted and should not be trusted.";
throw new SignatureException(msg);
}
// 하단 부분은 생략
코드를 읽어보면 대충 흐름이 잡힌다!
조작이 되었는지 어떻게 검증할까?
1) 토큰이 도착하면 헤더 + 페이로드 + secretKey를 통해 B라는 새로운 시그니처를 만든다.
2) 기존에 발급한 A 토큰의 시그니처와, 시그니처B가 동일한지 비교한다.
3) A 와 B 가 동일하다면 pass, 다르다면 signatureException을 발생시킨다.
특이점:
당연히 시그니처의 유효성을 먼저 확인하고, 토큰이 조작되었다면 헤더 + 바디를 까보지도 않을 거라고 생각했는데 반대였다.
1) jwt 형식 확인
2) 헤더 확인
3) 바디 확인
4) 시그니처 유효성 검증
의 순서를 거쳐서 토큰을 검증하는 코드를 위에서 찾아볼 수 있었다.
토큰이 조작되었는지 시그니처를 확인하는 흐름을 생각해보면 당연한 것 같다. 새로운 시그니처를 만들기 위해서 헤더를 까봐야 하니...
몰랐던 사실을 알게 되니깐 재밌당
'실험실' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DB 통신 중 연결이 끊긴다면 어떻게 될까? (feat. JPA) (0) | 2025.06.14 |
|---|
